Informatica Workflow Recovery with High Availability for Auto Restartable Jobs

Restartable ETL jobs are very crucial to job failure recovery, supportability and data quality of any ETL system. In one of our prior articles we discussed different design techniques for ETL restartability, independent of the ETL tool used. We can also implement restartability in an ETL job using Informatica PowerCenter workflow recovery capabilities. In this article lets see what is required to setup an informatica workflow for recovery.
What is Workflow Recovery
Workflow recovery allows you to continue processing the workflow and workflow tasks from the point of interruption. During the workflow recovery process Integration Service access the workflow state, which is stored in memory or on disk based on the recovery configuration. The workflow state of operation includes the status of tasks in the workflow and workflow variable values. The configuration includes.
- Workflow Configuration for Recovery
- Session and Tasks Configuration for Recovery
- Recovering the Workflow from Failure
1. Workflow Configuration for Recovery
To configure a workflow for recovery, we must enable the workflow for recovery or configure the workflow to suspend on task error.
Enable Recovery : When you enable a workflow for recovery, the Integration Service saves the workflow state of operation in a shared location. You can recover the workflow if it terminates, stops, or aborts. The workflow does not have to be running.
We can set up the automatic recovery in the workflow as shown in below image. 
Note : An optional High Availability (HA) license is required for this check box to be available for selection. Without the HA option, workflows must be recovered manually. That is, you must locate the failed workflow in the Workflow Monitor client and manually tell PowerCenter to recover the workflow or use the command line to recover the workflow.
Suspend : When you configure a workflow to suspend on error, the Integration Service stores the workflow state of operation in memory. You can recover the suspended workflow if a task fails. You can fix the task error and recover the workflow. If the workflow is not able to recover automatically from failure with in the maximum allowed number of attempts, it goes to 'suspended' state.
|
We can set up the workflow to suspend on error as shown in below image.


2. Session and Tasks Configuration for Recovery
Each session or task in a workflow has its own recovery strategy. When the Integration Service recovers a workflow, it recovers tasks based on the recovery strategy of each task or session specified. Three different options are available.
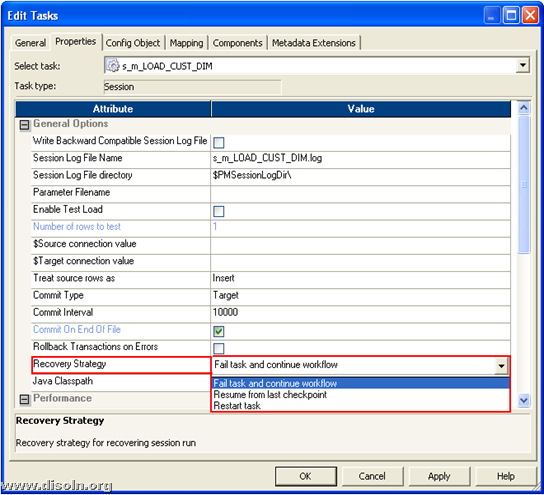
You can see the available command task recovery options as shown in below image.

- Restart task
- Fail task and continue workflow
- Resume from the last checkpoint
Restart task : This recovery strategy is available for all type of workflow tasks. When the Integration Service recovers a workflow, it restarts each recoverable task that is configured with a restart strategy. You can configure Session and Command tasks with a restart recovery strategy. All other tasks have a restart recovery strategy by default.
Fail task and continue workflow : This recovery strategy is only available for session and command tasks. When the Integration Service recovers a workflow, it does not recover the task. The task status becomes failed, and the Integration Service continues running the workflow. Configure a fail recovery strategy if you want to complete the workflow, but you do not want to recover the task.
Resume from the last checkpoint : This recovery strategy is only available for session tasks. The Integration Service saves the session state of operation and maintains target recovery tables. If the session aborts, stops, or terminates, the Integration Service uses the saved recovery information to resume the session from the point of interruption.
When you configure the session recovery strategy to resume from the last checkpoint, Integration Service stores the session state of operation in the shared location, $PMStorageDir. And also it is written to the recovery tables (PM_RECOVERY, PM_TGT_RUN_ID, PM_REC_STATE) to determine where to begin loading data to target tables, in case of a recovery.
You can see the available session recovery options as shown in below image.

You can see the available command task recovery options as shown in below image.

3. Recovering the Workflow from Failure
Workflow can be either recovered automatically or manually depending on the workflow recovery strategy
Recovering Automatically
If you have High Availability (HA) licence and the workflow is configured to recover automatically as described above, Integration service automatically attempts to recover the workflow based on the recovery strategy set of each session or task in the workflow. If the workflow is not able to recover automatically from failure with in the maximum allowed number of attempts, it goes to 'suspended' state, which can be then manually recovered.
Recovering Manually
If you do not have High Availability (HA) licence, you can manually recover the workflow or individual tasks with in a workflow separately. You can access the options as shown in below image from the workflow manager or from the workflow monitor.
Recover workflow :- Continue processing the workflow from the point of interruption.
Recover Task :- Recover a session but not the rest of the workflow.
Recover workflow from a task :- Recover a session and continue processing a workflow.

Hope this article is informative and useful for your projects. Please leave your comments and feedback.
